Introduction
Arduino is:
- A software environment
- A Company
- An assortment of hardware
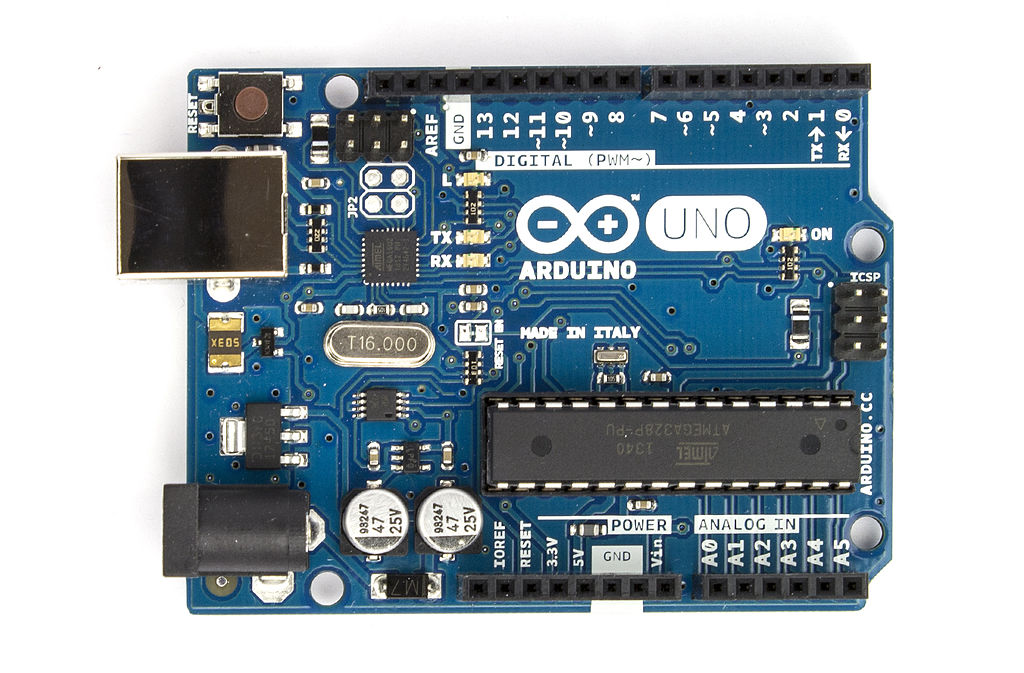
You’re experience with Arduino hardware is most likely related to the Arduino UNO board, which was released in 2010. It is developed by Arduino (the company) and is supported by the Arduino software environment. The UNO is slow, with a single 8 bit processor running at 16 MHz.
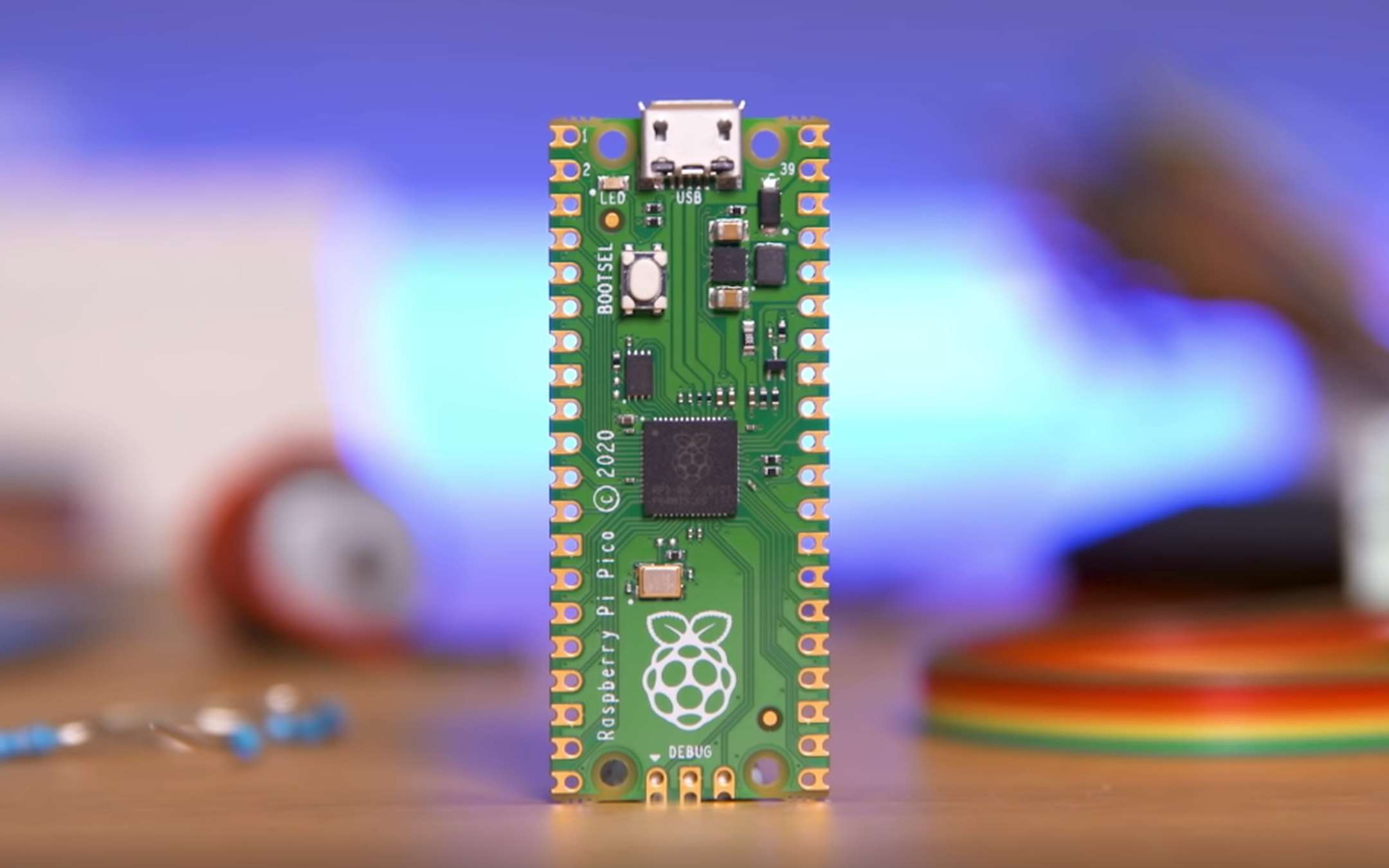
The Raspberry Pi Pico
Released by the Raspberry Pi Foundation in January 2021, the Pi Pico is much faster than the Arduino UNO, with two 32 bit cores running at 133 MHz. The Pico’s main processor is directly developed by the Raspberry Pi foundation itself. The Pico supports Arduino (the software environment) as well as MicroPython and has a very well maintained C/C++ toolchain.
Other Arduino Boards
There are lots and lots of other boards - often when building a project one chooses a board which has the right combination of special features like Wifi, Bluetooth, or battery support and the right amount of IO (input/output), and then picks the smallest of the suitable boards. For the purpose of learning Arduino, choose a general purpose board with enough processing power and IO to offset poor choices like an ESP32 or in this case, raspberry pi pico.
Lesson Summary
1. Arduino I/O
Things To Learn:
- Differences between and how to use
- GPIO
- I2C
- SPI
- Analog Input
How to Learn Those Things
- Connect Sensors Using
- I2C (GY521)
- SPI (MAX31855)
- Detect a button press using GPIO
- Blink an led using GPIO
- Read the voltage from a particular pin
2. Advanced Serial.print
Things To Learn:
- How to print variables
- What is
\n - How to format prints for use in the plotter
How to Learn Those Things
- Create “FizzBuzz” on an Arduino
- Print the values from the integrated temperature sensor and one ADC channel so both can be plotted
3. Ohms Law
Things To Learn:
- What is a resistor
- How to calculate the maximum current through a resistor
- How to calculate the voltage drop through a resistor
- Why are pull-up/down resistors used
How to Learn Those Things
- https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1g_VVW8MZelAA-1f9-P59pU53GeOMtEQPL9Q2TULZHAw/edit#slide=id.g2cb6c77c18d_0_229
- Do the math together on a whiteboard
4. Using Functional Outputs
Things To Learn:
- How to use
- Motors (H-Bridge)
- Servos (PWM)
- Relays
How to Learn Those Things
- Create a program which detects keywords in Serial.read to toggle a relay, spin a motor, and toggle a servo between two positions
5. Reading Schematics
Things To Learn:
- Symbols for
- Resistors
- Capacitors
- Batteries
How to Learn Those Things
6. Keyboard Library
Things To Learn:
- The difference between “pressing” and “sending” a keystroke
- Using the keyboard library to print text
- Using the keyboard library to act as an analog game controller
- Using the keyboard library to send keyboard shortcuts
How to Learn Those Things
- Create a “rubber ducky” program which changes the wallpaper of an attached windows computer
- Create a 2-axis game controller using an analog joystick