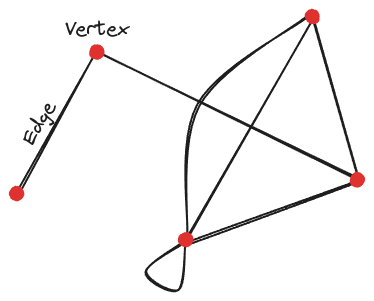
Vertex:
- A point
- AKA node
- Can have many edges
- The degree of a vertex counts the number of edges it connects to
- Looped back edges count twice
- “indegree” and “outdegree” count number of arrows pointing in or out (only for directed graphs)
Edge:
- Connects two vertexes
- Can loop back to the same vertex
- Multiple edges can connect between the same vertecies
Pigeon Hole Principle “A directed graph with n vertices and n edges, where each note has outdegree of 1 will always have between 1 and n cycles”
Size of a set is denoted by absolute value: is the size of the set of all men
Colleys Method Colley matrix times ranking matrix equals win/loss matrix
win/loss matrix is
multiply both sides by inverse of colley matrix to find ranking matrix
Graphs for division/allocation
Top Trading Cycle
- Everyone picks selects the thing they want most
- Search for cycles, swapping item
- Once cycles have been eliminated, people with no preference on the board pick a “next best option”
Stable Matching
- Matching between two separate groups (represented by bipartite graph)
- A pair includes one vertex from each set
- Stable if there are no rouges
- There are no people who prefer each other to the person they are currently matched with
Gale-Shapley
- Matching between two separate groups (represented by bipartite graph)
- One side proposes, other side accepts or not, or temporarily accept
- As more proposals are made, accepters have the opportunity to reconfigure
- Can be different if sides are swapped
- Stable
- The proposers get they first compatible choice - optimal
- The Accepters get to keep the